This blog post is part of “The Ultimate Guide to SEO” blog series.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a large distributed system of servers deployed in geographically distributed data centers to ensure that your site loads fast from anywhere in the world. The result is that content loads faster because copies of it are stored closer to the end-user, and your site easily adjusts to traffic spikes because the global network of servers shares the traffic load.
According to Builtwith, more than 40 percent of the top 10,000 websites use a CDN, while just 3 percent of the entire internet use a CDN. The average size of a web page has grown some 240 percent, straining page speed.
A CDN works as follows. A user enters the address of a website in a browser, which initiates a request for all of the assets that make up the requested page. The first request for each element on the page is sent to the primary server. The CDN’s edge server closest to the user then caches a copy of the static elements of the page that are sent from the primary server to the user. Future requests for the same page are delivered via the CDN server where the elements are cached instead of via the primary server.
Site Speed and SEO
A CDN can help with a website’s search engine rankings in two ways. First, as user experience becomes a greater factor in how search engines rank web pages, fast pages make users happier than slow ones, and faster page speeds will increase your SEO juice accordingly. Secondly, as SEO Journal reports, “CDNs use caching algorithms and canonical headers to help enhance SEO of your website by combatting duplicate content creation issues.” Search engines frown on duplicate content.
Site Speed and Revenue
A 2014 study by Akamai found that web users expect websites to load in 3 seconds or less. At the time, the top 500 e-commerce sites in the world had a median load time of about 10 seconds.
It has been proven that by boosting the speed of a website, you can dramatically improve conversion rates and revenue. The study found that shaving just one second off page load times can increase conversions by 7 percent. One study found that Walmart lost 1 percent of revenue for every 100ms of page loading delay, and that the company gained 2 percent of revenue for every 1-second improvement in page loading times.
Scalability and Security
Using a CDN also makes it much easier to absorb sudden or unexpected increases in traffic, as the CDN can be configured to share the extra load among multiple server locations. Also, if there is a website outage or attack and the host server goes down or is impaired, the copies of the pages will still be accessible on at least some of the CDN servers.
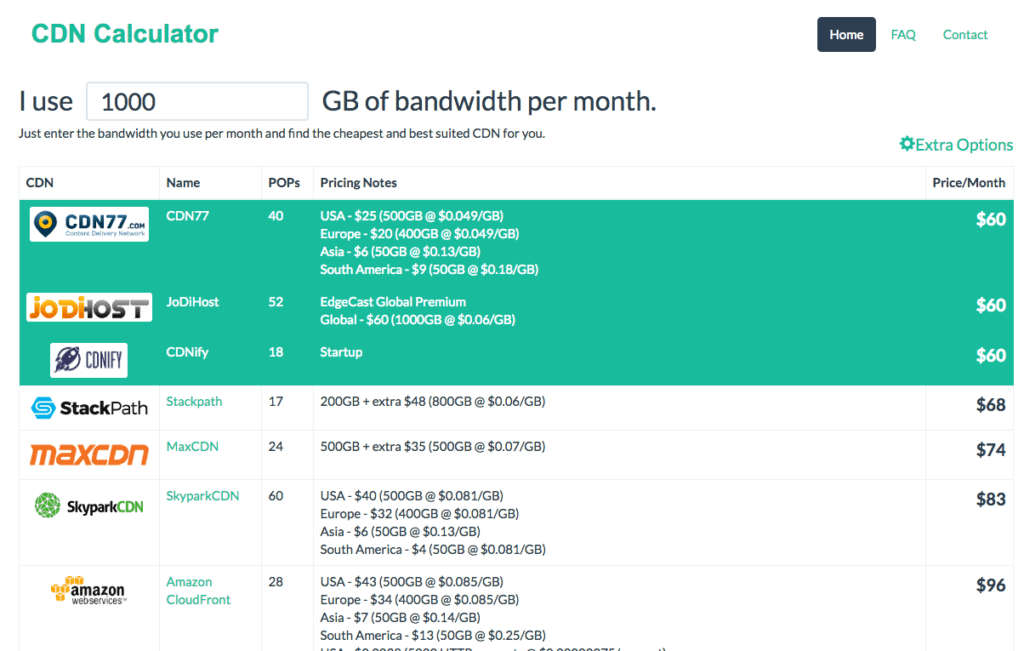
CDN Pricing
CDN is sold as a service by hosting and cloud computing companies. The cost of a CDN is typically based on the amount of data transfer that you will require and the number of regions around the world in which you want to make your site available. Some hosting services like WPengine (our favorite) include a CDN in some if its hosting packages. CDN calculator can give you at least a ballpark price, but beware that the features of each CDN provider may vary, making head-to-head comparisons difficult.
Bottom Line Benefits
For businesses that rely on web traffic for leads and sales, page loading speed is critical for both SEO and for conversions. A CDN can help increase page loading speeds, and for e-commerce sites, the revenue that comes along with it.




